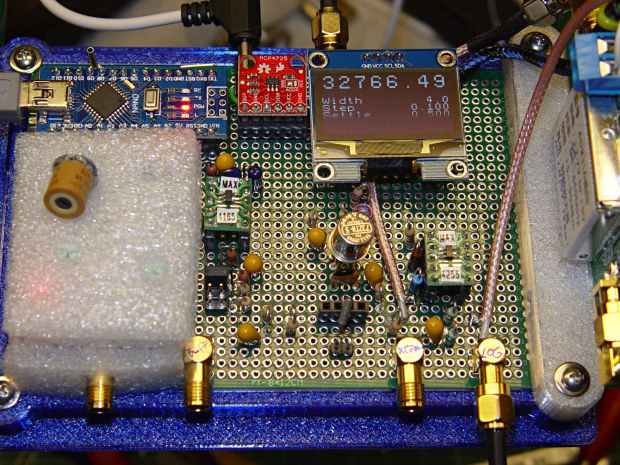
The Big Ideas: the DDS output, being more-or-less constant, needs a variable-gain amp to set the crystal drive level. The amp also fixes the impedance mismatch between the DDS output and the crystal, which may not be much of a problem for the (very) high ESR quartz tuning fork resonators in play.
The AD9850 DDS output feeds a 70 MHz (-ish) elliptical reconstruction filter chopping off image frequencies descending from the 125 MHz sampling clock, with a 100 Ω (-ish) output impedance that’s just about purely resistive at 60 kHz. An on-board 3.9 kΩ resistor (labeled with 392 on their schematic) sets the full-scale output current to 10 mA for a peak voltage of 1 V. The module uses only the + output of the differential pair, which means the sine wave runs from 0 V to 1 V: 1 Vpp = 500 mVpeak = 353 mVrms (ignoring the 500 mV offset).
Pin header J3 normally sports a jumper to connect the 3.9 kΩ RSET resistor, but you can insert an external resistor to increase the resistance and decrease the output current:
IOUT = 32 × 1.248 V / RSET
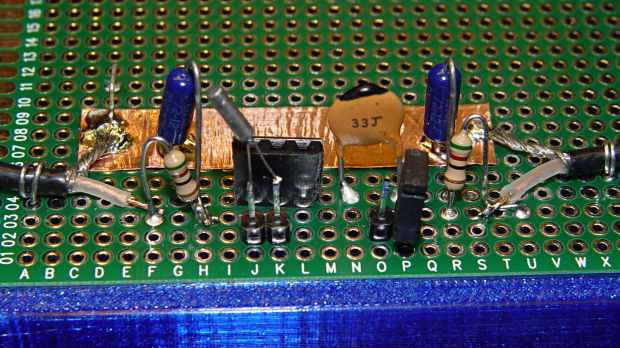
A little hot-melt glue action produced a suitable lashup from a 5 kΩ trimpot:

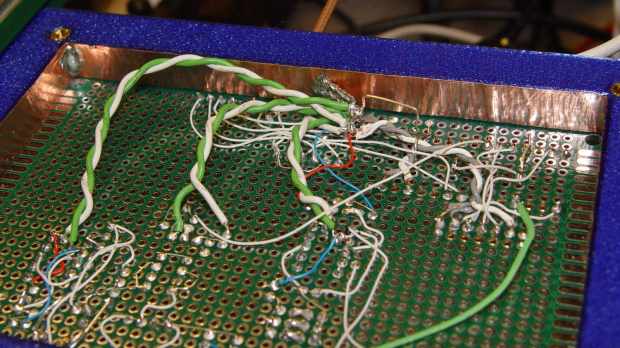
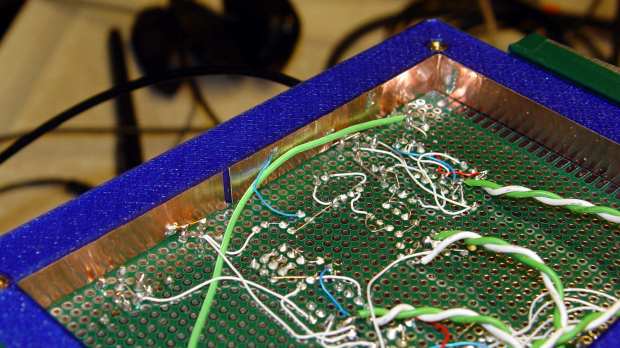
The pillars of green wire insulation forestall screwdriver shorts to the bare pin headers, although that’s less of risk with the upper insulating foam sheet in place:

A 5 kΩ trimpot can vary the output voltage downward by a factor of 2 = -6 dB, more or less.
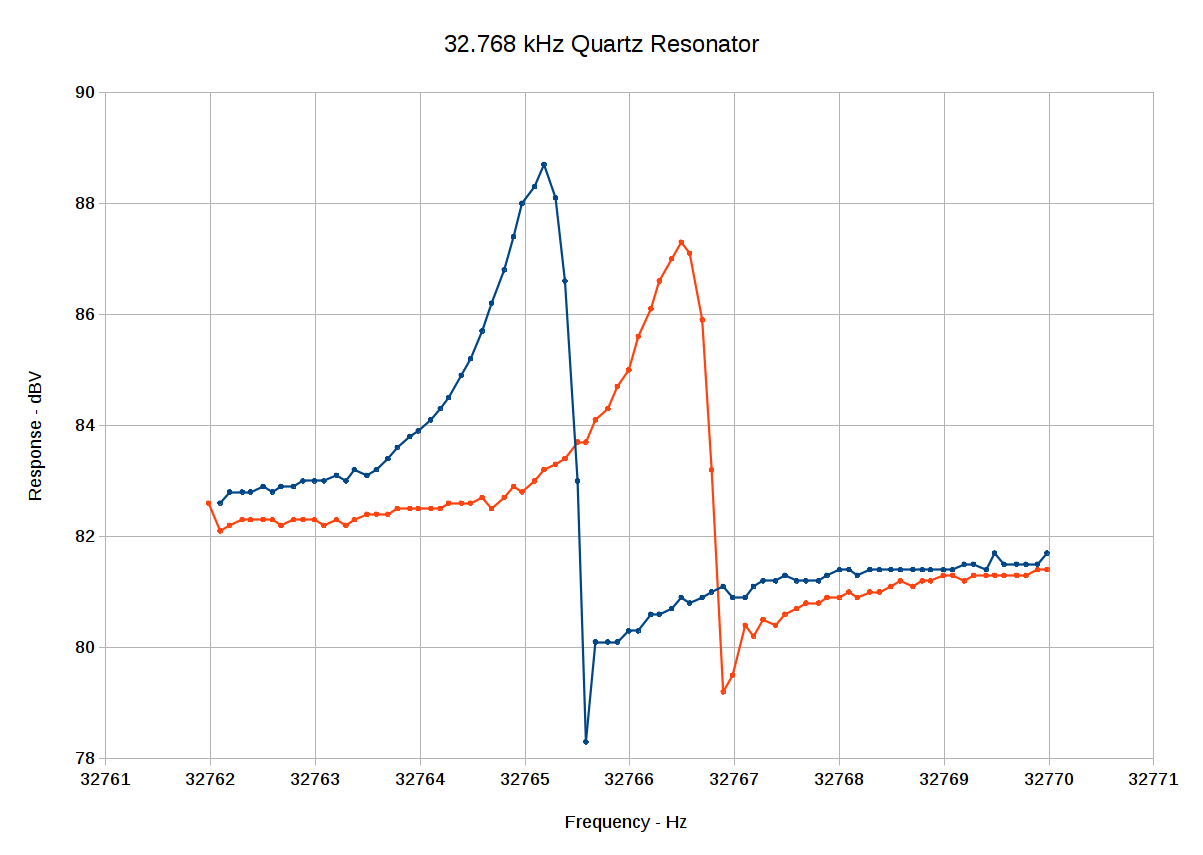
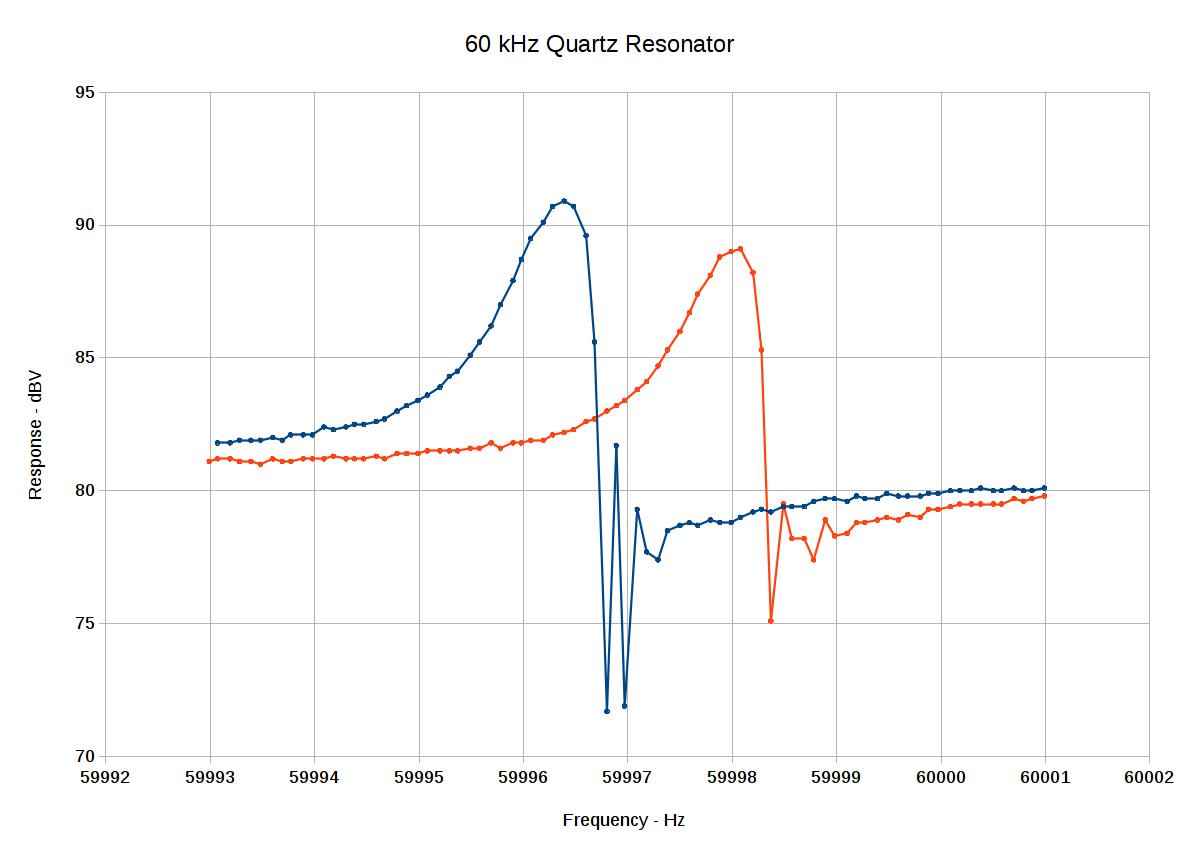
All the quartz tuning fork resonator specs I’ve found, none of which may apply to the units on hand, seem to require no more than 1 µW drive. Given a resonator’s equivalent series resistance of around 20 kΩ (for real!), the drive voltage will be 150 mV (-ish):
1 µW = V² / 20 kΩ, so V = sqrt(20×10³) = 141 mV
The nominal version of the crystal tester had a 50 Ω input impedance, so I picked a MAX4165 op amp with mojo sufficient for anything over 25 Ω; in retrospect, a lighter load than 48 Ω would be fine.
In any event, the amp looks like this:

What looks like a DIP switch is really the 3×2 jumper header just to the right of the foam insulation, in front of the SOT23 space transformer PCB carrying the MAX4165. No jumper = 0 dB gain, then 6 dB steps upward from there. The -6 dB trimpot range gives more-or-less continuous output tweakage across 24 dB, -6 dB to +18 dB, which is certainly excessive. The 24 Ω terminating resistors provide 6 dB loss into the crystal, so the effective range is -12 to +12 dB, with 0 dB = 350 mVrms and -6 dB = 150 mVrms (-ish) at the crystal.
It’s a non-inverting amplifier, which (also in retrospect) probably isn’t a win:
- Yet Another Bypass Cap on the cold end of the gain-setting resistors
- Overly elaborate VCC/2 biasing to maintain sufficiently high input impedance
I’m reasonably sure all those big caps contribute to some low-level motorboating, but haven’t tracked it down.