-
Arduino Library for (Old?) Optrex DMC-family LCDs
Having determined that the existing Arduino LiquidCrystal library routine wouldn’t work for the Optrex DMC-16117 character LCD in my parts heap, I decided to modify it to meet the data and timing requirements mentioned in the datasheet. This is sufficiently slow and old that it should work for contemporary displays built around the Hitachi HD44780 and its ilk, but I certainly haven’t tested it!
The straight dope on building an Arduino library from scratch is there, but there’s no need to work from First Principles here.
Start by copying the library files (this FLOSS stuff is wonderful that way), renaming them, and changing all the LiquidCrystal strings to LCD_Optrex:
cd /opt/arduino/hardware/libraries/ cp -a LiquidCrystal LCD_Optrex cd LCD_Optrex rm LiquidCrystal.o rename 's/LiquidCrystal/LCD_Optrex/' LiquidCrystal.* for f in LCD* k*; do sed -i 's/LiquidCrystal/LCD_Optrex/g' $f; done cd examples for f in * ; do sed -i 's/LiquidCrystal/LCD_Optrex/g' $f/$f.pde cd -
You could do that by hand with an editor if you prefer.
Depending on how you’ve installed the Arduino files, you may need a sudo to make that work. Better, perhaps, to tweak the permissions for (at least) the LCD_Optrex directory & files therein to grant yourself write access.
I created a sendraw4() function to send a single 4-bit nibble during the startup sequence, so add that to the private section of LCD_Optrex.h:
private: void send(uint8_t, uint8_t); void sendraw4(uint8_t);
The new code is in LCD_Optrex is shamelessly adapted from the existing send() function, minus the mode selection and 8-bit stuff:
void LCD_Optrex::sendraw4(uint8_t value) { digitalWrite(_rs_pin, LOW); digitalWrite(_rw_pin, LOW); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { digitalWrite(_data_pins[i], (value >> (i + 4)) & 0x01); } digitalWrite(_enable_pin, HIGH); digitalWrite(_enable_pin, LOW); }If I were doing this from scratch, I’d use d7 through d4 rather than d3 through d0 to match the datasheet, but that’s a stylin’ thing.
Replace the existing LCD panel setup code with an exact mapping of the datasheet’s procedure. For the 4-bit setup, it goes a little something like this:
delayMicroseconds(16000); // mandatory delay for Vcc stabilization sendraw4(0x30); // set 8-bit mode (yes, it's true!) delayMicroseconds(5000); // mandatory delay sendraw4(0x30); delayMicroseconds(200); sendraw4(0x30); delayMicroseconds(40); // command delay sendraw4(0x20); // finally set 4-bit mode delayMicroseconds(40); // command delay command(0x28); // 4-bit, 2-line, 5x7 char set command(0x08); // display off command(0x01); // clear display delayMicroseconds(16000); command(0x06); // increment, no shift command(0x0c); // display on, no cursor, no blink
It seems you cannot use the delay() function in the constructor, as interrupts and suchlike aren’t active. The delayMicroseconds() function disables & enables interrupts; I don’t know if that is a Bad Thing or not.
The 8-bit initialization code, which I haven’t tested, doesn’t need the sendraw4() function, but does need the same alterations. Apart from enabling 4-bit mode, of course.
Various commands have different timing requirements, as shown on page 39 of the DMC16117 datasheet. Add a delayMicroseconds(16000); to the clear() and home() functions, then add delayMicroseconds(40); to the send() function, like this:
void LCD_Optrex::clear() { command(0x01); // clear display, set cursor position to zero delayMicroseconds(16000); }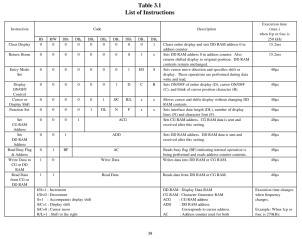
Optrex DMC16117 Instruction Timing With all that in place, fire up the Arduino IDE and compile one of the example programs. That will build the LCD_Optrex.o file, too. If you have such a display, either wire it up as indicated or change the example code to match your connections.
What should happen is that the LCD should initialize correctly under all conditions… how’s that for anticlimactic?
Here’s an OpenOffice document with LCD_Optrex.h, LCD_Optrex.cpp, and examples.txt all in one lump: LCD_Optrex Library Files.odt. Save each section as a separate flat-ASCII text file with the appropriate name in the right spot and you’re in business. I’d present a ZIP file, but WordPress isn’t up to that.
Memo to Self: A function to write a 16-character string to the stupid 16-character DMC16117 which has a single row that’s addressed as two 8-character lines would be nice. That requires keeping track of the current cursor position, which could be tricky. Maybe I should just scrap those suckers out?
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.